What’s a family business?
A family business is a commercial organization in which decision-making is influenced by multiple generations of a family—related by blood or marriage. They are closely identified with the firm through leadership or ownership. Owner-manager entrepreneurial firms are not considered to be family businesses because they lack the multi-generational dimension and family influence that create the unique dynamics and relationships of family businesses. … Wikipedia
Other definitions are more general, describing a family business as one that is owned OR operated by one’s family. Business families and family businesses fit into the 3 circle model shown below.
Note: We introduced the 3 circle model in a previous article
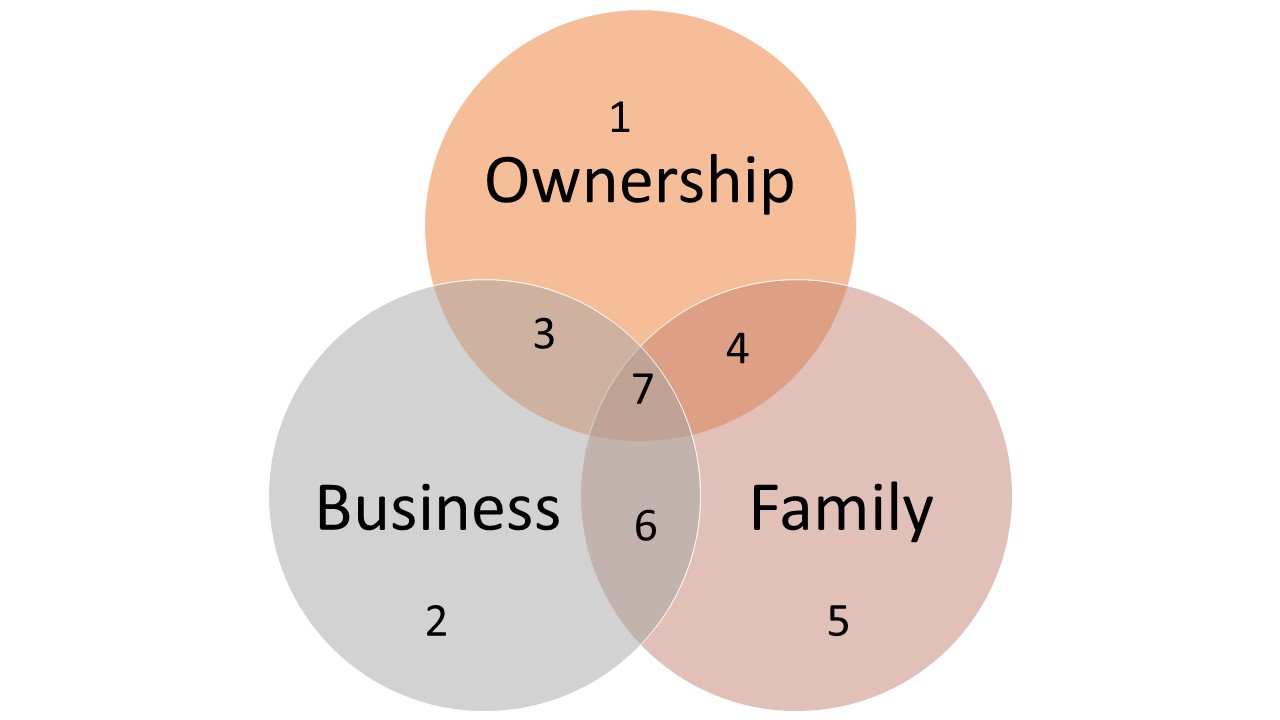
3 circle model for family business
FAMILY CIRCLE
Family / Owner Intersection (4) – these members own shares of the business and are members of the family but are not involved in operating or working in the business. They may have inherited shares, own shares as part of an estate plan or have invested in the business.
Family Only (5) – the members in this group are family members who are not owners and do not work in the business. These may be children, siblings, cousins, spouse or other members of “family”.
Family / Employee (Business) Intersection (6) – Individuals in this area are family members who work in the business but have no ownership of the business. These can include the spouses of the owner(s), children, siblings, nephews, nieces, or other family members.
Family/Employee/Owner (7) – This is the “sweet spot” where a relatively few members of the family wear all hats. These individuals are family members, owners and work in the business in an operational or management role.
BUSINESS (EMPLOYEE) CIRCLE
Business (Employee) Only (2) – Individuals in this area are not family members but are employees. They often have fewer opportunities for advancement as family members are often recruited into leadership roles. Implementing an employee performance management process and reward/compensation program that is perceived as fair to both groups of employees is often a challenge.
Business (Employees) & Owners (3) – In order to retain key non-family talent, employees may be given the opportunity to buy shares of the business through an employee stock option plan or other vehicles. This is often a vehicle used in succession planning when employees purchase the business from current owners.
Business (Employees) & Family (6) – as previously described
Business (Employees), Family & Owner (7) – as previously described
OWNER CIRCLE
Owner only (1) – individuals are investors but are not actively involved in the operations or members of the family. They may hold seats on the board of directors and may represent equity groups such as venture capital funds, crowdfunding platforms, etc.
Owner & Business (Employee) (3) – as previously described
Owner & Family (4) – as previously described
Owner, Business (Employee) & Family (7) – as previously described
Typically, individuals in the “family only” area are not considered to be participants in a “family business”. In our experience, these individuals are critical to the success of a family business especially if they are the immediate family of the individuals in the owner/employee/family zone. Keeping the family and business in-sync is what we refer to as the Family + Business circumstance.

Comments are closed